Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Terashima, Motoki; Saito, Takumi*; Ito, Miki*; Akagi, Yosuke*; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Soler, J. M.*; Martin, A. J.*; Lanyon, G. W.*; Havlov , V.*; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Tachi, Yukio
, V.*; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
An in-situ long-term diffusion (LTD) project has been performed at the Grimsel Test Site, Switzerland, to realistically evaluate matrix diffusion of radionuclides in crystalline rock with minimal disturbance to in-situ conditions. A second in situ diffusion experiment (monopole 2) has been performed. Predictive calculations for the monopole-2 experiment, based on results from monopole 1 or from through-diffusion experiments have been compared to monitoring data from the injection and observation boreholes. For the non-sorbing tracers (HTO,  Cl
Cl ), the diffusion parameters from the through-diffusion experiments provide a better match for the measurements, especially in the injection borehole. The initial drop in activities for
), the diffusion parameters from the through-diffusion experiments provide a better match for the measurements, especially in the injection borehole. The initial drop in activities for  Cs
Cs and
and  Ba
Ba shows clearly the effect of sorption. Bulk rock parameters for
shows clearly the effect of sorption. Bulk rock parameters for  Cs
Cs from monopole 1 seem to be applicable to monopole 2. However,
from monopole 1 seem to be applicable to monopole 2. However,  Ba
Ba seems to sorb more strongly than expected.
seems to sorb more strongly than expected.
Soler, J. M.*; L fgren, M.*; Nilsson, K.*; Lanyon, G. W.*; Gylling, B.*; Vidstrand, P.*; Neretnieks, I.*; Moreno, L.*; Liu, L.*; Meng, S.*; et al.
fgren, M.*; Nilsson, K.*; Lanyon, G. W.*; Gylling, B.*; Vidstrand, P.*; Neretnieks, I.*; Moreno, L.*; Liu, L.*; Meng, S.*; et al.
no journal, ,
The GWFTS Task Force is an international forum in the area of modeling of groundwater flow and solute transport in fractured rock. The WPDE experiments are matrix diffusion experiments in gneiss performed at the ONKALO underground facility in Finland. Synthetic groundwater containing several conservative and sorbing radiotracers was injected along a borehole interval. The objective of Task 9A of Task Force was the predictive modeling of the tracer breakthrough curves from the WPDE experiments. Several teams, using different modeling approaches, participated in this exercise. An important conclusion from this exercise is that the modeling results were very sensitive to the magnitude of dispersion in the borehole opening, which is related to the flow of water. Focusing on the tails of the breakthrough curves, which are more directly related to matrix diffusion and sorption, the results from the different teams were more comparable.
Sugiura, Yuki; Tomura, Tsutomu*; Doi, Reisuke; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Tachi, Yukio
no journal, ,
Tachi, Yukio; Ito, Tsuyoshi; Akagi, Yosuke*; Sato, Hisao*; Martin, A. J.*
no journal, ,
The effects of heterogeneity at fracture surface on radionuclides migration in fractured crystalline rocks was investigated by laboratory migration experiments, microscopic observations and detailed modelling, using a single fractured granodiorite sample from the Grimsel Test Site (GTS), Switzerland. The tracer migration behaviors in fracture and matrix parts were evaluated by series of laboratory experiments including through-diffusion and flow-through experiments. Mineral distributions from fracture surface to matrix were evaluated by X-ray CT, and were validated by comparing the elemental mapping measured by EPMA. Based on the microscopic observations by X-ray CT and EPMA, the aperture and connectivity in fracture and minerals distribution near fracture surface were quantitatively evaluated. The heterogeneous multi-layered model assuming a weathered vermiculite zone, a foliated mica zone and rock matrix was possible to provide a reasonable interpretation for measured breakthrough curves of all tracers.
Tachi, Yukio; Ito, Tsuyoshi; Gylling, B.*
no journal, ,
The in-situ long-term sorption and diffusion experiment (LTDE-SD) at the Aspo Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden provides valuable dataset to test the scaling approach from laboratory to in-situ condition. The scaling approach developed in the in-situ Long-Term Diffusion (LTD) project at Grimsel Test Site in Switzerland was tested for the LTDE-SD results as part of the SKB Task Force on modeling of groundwater flow and transport of solutes in fractured crystalline rocks. Our modelling approach could account reasonably overall trends for sorption and diffusion of 10 radionuclides, and was then evaluated as being applicable for a wider range of radionuclides and for more complex fracture systems.

 /HSe
/HSe ) system determined by cyclic voltammetry
) system determined by cyclic voltammetryDoi, Reisuke; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
In the calculation of HSe - Se
- Se
 ratios in repository groundwaters, the reliability of the results depends on that of the standard redox potential of the HSe
ratios in repository groundwaters, the reliability of the results depends on that of the standard redox potential of the HSe /Se
/Se
 couple. Therefore, cyclic voltammetry has been carried out to determine this potential. The redox potential of the solution bulk was controlled to ensure that HSe
couple. Therefore, cyclic voltammetry has been carried out to determine this potential. The redox potential of the solution bulk was controlled to ensure that HSe was the predominant dissolved species, followed by cyclic voltammetry to obtain the cylcic voltammogram assigned as arising from the reaction: Se
was the predominant dissolved species, followed by cyclic voltammetry to obtain the cylcic voltammogram assigned as arising from the reaction: Se
 +4H
+4H +6e
+6e
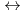 4HSe
4HSe . The half-wave potentials were measured as a function of the molality of Na
. The half-wave potentials were measured as a function of the molality of Na . The standard potential was derived from the Na
. The standard potential was derived from the Na concentration dependence of the half-wave potential.
concentration dependence of the half-wave potential.
Tanaka, Kazuya; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Takahashi, Yoshio*
no journal, ,
We analyzed fresh and dead leaves of Cryptomeria japonica collected in forests in Fukushima after the Fukushima accident using autoradiography. The distribution of radioactivity in the leaf samples indicates that particulate forms of radiocesium were deposited on forests. Leaching with pure water removed both soluble and insoluble particulate fractions of radiocesium from the surface of the contaminated leaves, but significant amounts of radioactivity remained. This suggests that foliar absorption occurred in both fresh and dead leaves. Further leaching treatments using surfactant and acetone could not remove the remaining radiocesium from the leaves. The leaching experiments indicate that radiocesium in the contaminated leaves was strongly fixed or solely stayed inside leaf tissues, and not readily released outside unless leaf tissues are decomposed.
Iijima, Kazuki; Kitamura, Akihiro; Miyahara, Kaname
no journal, ,
Understandings of transport behaviour of radiocesium in the environment were overviewed, and distribution of other radionuclides was compared to that of radiocesium. Annual discharge of radiocesium from forest with soil particles and fine litter were around 0.1% of those of initially deposited and independent to vegetation and slope if there was enough litter and small plants. In the stream water taken nearby the flowing out point showed higher concentration of dissolved radiocesium that that of groundwater, suggesting that dissolved radiocesium was generated due to the degradation of litter or the desorption from soil and dissolved. The concentration of dissolved radiocesium in river water was lower than 1 Bq/L in all river systems. Since the direction dependency on the off-site distribution of these radionuclides were similar to that of observed in the FDNPS site, the estimation of the on-site distribution based on the off-site one was considered to be available.